
Method of Using Dual Responsive Polymers as Draw Solutes for Forward Osmosis Desalination
Synopsis
This invention enhances forward osmosis desalination by introducing a novel draw solute comprising carbon dioxide and thermally responsive units. This dual-responsive solute can reversibly switch between protonated and deprotonated states, enabling a more efficient osmosis method.
Opportunity
Forward osmosis (FO) desalination offers a promising alternative to traditional reverse osmosis systems, consuming less energy and reducing membrane fouling. The key to its effectiveness lies in the use of a specialised draw solute that can easily move water molecules from a less concentrated feed solution to a more concentrated draw solution, subsequently allowing for the easy and reuse of the draw solute to produce clean, treated water.
Technology
The present technology introduces a draw solute specifically designed for forward osmosis, integrating carbon dioxide and responsive structural units. This composition enables the solute to respond efficiently to changes in environmental conditions, switching between a protonated state and a deprotonated state as needed. This feature makes the draw solute highly effective and reusable within the forward osmosis membrane process.
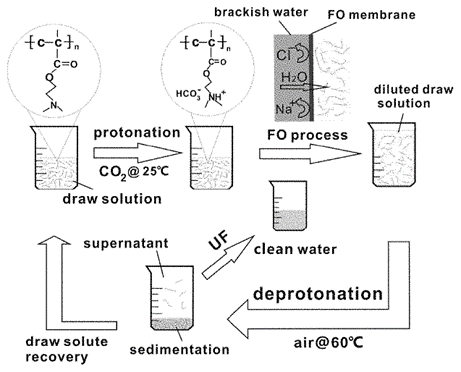
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of a forward osmosis method according to a particular embodiment of the present invention.
Applications & Advantages
- The ability of the draw solute to switch between protonated and deprotonated states allows it to adapt dynamically to varying operational conditions, thus improving the efficiency of the osmosis desalination process.
- By offering adjustable molecular weights, this technology allows for customisation to suit specific forward osmosis applications, optimising performance and efficacy.
- The draw solute is specifically designed to be compatible with forward osmosis systems, providing a robust and innovative solution to modern water treatment challenges.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=29c7e020_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)
-and-the-coated-wood-(ntu-singapore).tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=624bb80c_1)









