
EchoLoc: Infrastructure-Free Smartphone Indoor Localisation System Using Room Acoustic Responses
Synopsis
EchoLoc is a smartphone indoor localisation system using echoes to pinpoint locations without the need for additional infrastructure. EchoLoc can support various location-based mobile services such as navigation, workspace clock-in, artwork interaction and emergency response.
Opportunity
Smartphone-based localisation technology has attracted wide attention in recent years driven by the widespread adoption of smartphones and the growing demand for location-aware services. In indoor environments, the limitations of the global positioning system (GPS) often render it unavailable due to signal blockage, prompting the need for alternative wireless indoor positioning solutions. Modalities such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have been leveraged to create smartphone-based indoor localisation systems, typically relying on infrastructure such as anchor points. However, the extensive infrastructure installation required by these traditional solutions often hinders their widespread applicability.
In response to these challenges, there is a growing preference for accurate and reliable infrastructure-free indoor localisation systems. To that end, we have designed EchoLoc, a deep neural network (DNN)-based system for accurate and large-scale smartphone indoor localisation using room acoustic responses. EchoLoc operates by controlling the smartphone's audio system to emit nearly inaudible chirps and record the resulting echoes. These echoes are then processed by a cloud-hosted DNN for location inference, with the results transmitted back to the mobile EchoLoc Client.
Technology
EchoLoc consists of two key components: the EchoLoc Client and the EchoLoc Server. The EchoLoc Client is a mobile application used for both data collection and real-time localisation. In the training mode, it emits inaudible chirps, records corresponding acoustic traces, and sends data with location labels to the server for model training. It is worth noting that a robot can be used to navigate indoor spaces for efficient data collection. In the inference mode, the client transmits chirps and acoustic traces to the server, which promptly provides the predicted location. This location is then displayed on the smartphone screen for user visualisation.
The EchoLoc Server operates in the cloud, through a customised DNN architecture that accepts acoustic spectrogram features as input. In the training mode, the server first pre-processes the echo traces to generate echo features, and then performs model training using the pre-processed data. In the inference mode, it feeds the pre-processed fingerprints into the DNN, and outputs the corresponding prediction results. To achieve more reliable localisation results, the server performs a majority vote based on the predicted results for multiple chirps at certain location, before it returns the voting result to the client.
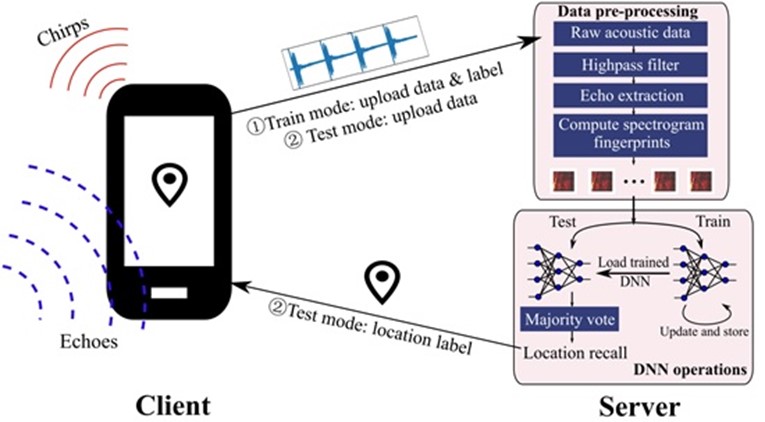
Figure 1: Workflow of EchoLoc.
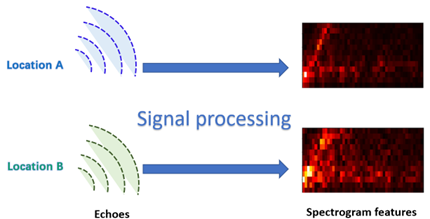
Figure 2: Different locations have different echo features.
Applications & Advantages
- EchoLoc is infrastructure-free and works with normal hand grasping of the smartphone.
- EchoLoc emits chirps in a frequency range from 15 kHz to 20 kHz, which is inaudible to human ears. Therefore, EchoLoc is robust to ambient noise and causes little/no annoyance to users.
- EchoLoc achieves 95% location recall accuracy in a large public indoor space and sub-metre mean localisation error in the tested lab office. This localisation accuracy can support a range of location-based mobile services, such as navigation, wayfinding, workspace clock-in, artwork interaction, emergency response, and more.














/enri-thumbnails/careeropportunities1f0caf1c-a12d-479c-be7c-3c04e085c617.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=d7261e3b_1)

/cradle-thumbnails/research-capabilities1516d0ba63aa44f0b4ee77a8c05263b2.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=1bc94f8_1)

7e6fdc03-9018-4d08-9a98-8a21acbc37ba.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=7deaf618_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=414f0d90_1)








