
Design Strategy for Pt/C Electrocatalysts Based on Hydrogen Spillover
Synopsis
Green hydrogen production utilises platinum (Pt) catalysts like Pt nanoparticles (NPs) on carbon. This innovation employs hydrogen spillover for a synergistic Pt-carbon interaction, thereby enhancing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). This approach overcomes the limitations of currently available designs which lack efficient Pt utilisation.
Opportunity
Green hydrogen fuel presents a promising remedy for the prevailing energy crisis and climate change concerns. The platinum (Pt)-based catalyst stands out as the most effective catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) due to its optimised hydrogen adsorption energy. State-of-the-art commercial catalysts in water electrolysers involve the use of highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles (NPs) anchored onto mesoporous carbon. However, the existing design strategy falls short in achieving a platinum-based catalyst with nearly 100% surface atom utilisation efficiency. Moreover, the carbon support is typically regarded as a passive participant, not directly contributing to HER.
This innovation introduces a novel electrocatalyst that leverages the synergistic interaction between Pt and the carbon support, specifically through hydrogen spillover. This approach enhances the efficiency of HER and maximises the utilisation of platinum.
Technology
The technology involves a new electrocatalyst which enables synergetic effect of Pt and carbon support, namely hydrogen spillover, to improve HER efficiency and utilisation of Pt.
A hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst expedites the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in water electrolysis, where an electric current splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. The electrocatalyst operates at the cathode, facilitating the reduction of hydrogen ions (H+) to hydrogen gas (H2). By lowering the activation energy needed for HER, the electrocatalyst enhances efficiency and boosts the rate of hydrogen gas production.
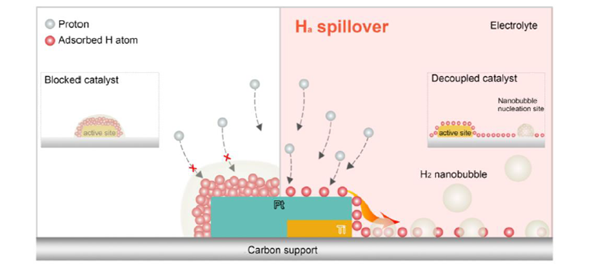
Figure 1: The hypothesis of decoupled-hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) induced by hydrogen spillover in Pt/C system.
Applications & Advantages
Understanding gained from electrocatalysts based on hydrogen spillover can guide the creation of materials that are both efficient and economical for a range of renewable energy devices, including alkaline fuel cells and electrolysers.
Advantages:
- Increased active sites for hydrogen production leading to significant increased performance with an ~80-fold increase at -50mV vs RHE and a ~50-fold increase at -100 mV vs RHE relative to reported pure Pt film.
- Reduced energy loss.
- Decrease cost due to efficient use of Pt.














/enri-thumbnails/careeropportunities1f0caf1c-a12d-479c-be7c-3c04e085c617.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=d7261e3b_1)

/cradle-thumbnails/research-capabilities1516d0ba63aa44f0b4ee77a8c05263b2.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=1bc94f8_1)

7e6fdc03-9018-4d08-9a98-8a21acbc37ba.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=7deaf618_1)



.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=b5366f51_1)
.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)
-and-the-coated-wood-(ntu-singapore).tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=624bb80c_1)








