
Self-Pumping Magnetic Cooling System
Synopsis
Magnetic cooling technology leverages the magnetocaloric effect, where a magnetic material heats up and cools down in response to a changing magnetic field. This offers an efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cooling methods. With diverse potential applications across industries, magnetic cooling systems eliminate the need for refrigerants and compressors.
Opportunity
Magnetic cooling is a promising technology with vast potential applications across various industries. Unlike conventional cooling methods that rely on refrigerants and compressors, magnetic cooling systems harness the magnetocaloric effect for efficient cooling. The process involves exposing a magnetic material to a changing magnetic field, causing it to heat up and subsequently cool down when the field is removed. This approach not only offers an environmentally friendly solution but also presents an alternative to energy-efficient cooling.
A patent for this technology has been filed; please refer to this link for further details.
Technology
Our magnetic cooling system pertains to the development of a dual-function device that facilitates simultaneous magnetic cooling and self-pumping. Leveraging the change in magnetisation of ferrofluid with temperature, the system's performance hinges on factors such as heat load, magnetic particle content, magnetic field and device shape. Designed as a self-regulating system, an increase in heat load amplifies the driving force for fluid motion, thereby enhancing heat transfer from the heat source to the sink. Notably, the system operates without the need for external pumps, achieving a more compact, noise-free and vibration-free energy-efficient cooling systems.
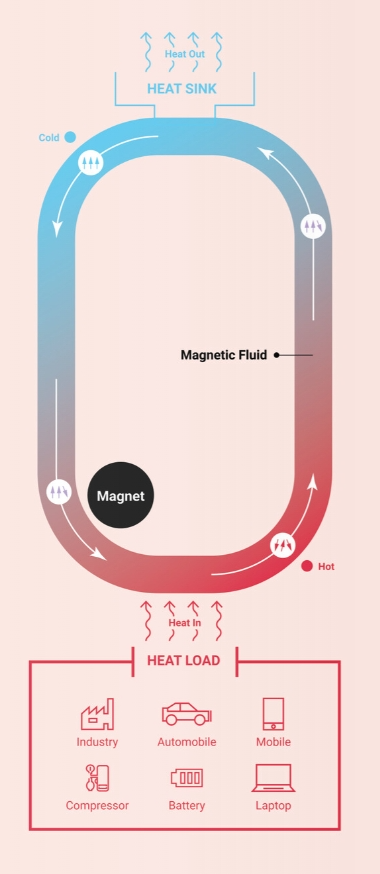
Figure 1: Self-pumping energy efficient magnetic cooling system
Applications & Advantages
- No pumps required—ferrofluid flow is driven mainly by magnetothermal effect.
- Cost-effective and can versatile applicability, including in electronic systems and buildings.














/enri-thumbnails/careeropportunities1f0caf1c-a12d-479c-be7c-3c04e085c617.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=d7261e3b_1)

/cradle-thumbnails/research-capabilities1516d0ba63aa44f0b4ee77a8c05263b2.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=1bc94f8_1)

7e6fdc03-9018-4d08-9a98-8a21acbc37ba.tmb-mega-menu.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=7deaf618_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)
-(2).tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=aa22bd90_1)
-and-the-coated-wood-(ntu-singapore).tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=624bb80c_1)










