
3D LiDAR-Based Autonomous Navigation and Collision Avoidance for Autonomous Mobile Robots
Synopsis
3D light detection and ranging (LiDAR)-based technology enhances warehouse efficiency and safety with precise navigation and robust collision avoidance. Utilising detailed 3D maps, this technology allows autonomous robots to operate effectively in various lighting conditions, without reliance on pre-installed infrastructure.
Opportunity
3D LiDAR-based navigation and collision avoidance technology represents a cutting-edge solution in warehouse manipulation, significantly enhancing efficiency and safety. By generating detailed 3D maps of the environment, autonomous vehicles and robots can navigate with precision. This technology’s robust collision avoidance capability allows it to detect potential obstacles, both stationary and dynamic, ensuring safe and efficient operation. The applications in warehouses are extensive, including tasks like inventory retrieval, sorting and goods transportation. In large distribution centres, 3D LiDAR-equipped robots can optimise the supply-chain process by reducing the time needed to locate and transport items. The technology's adaptability to various lighting conditions and non-reliance on pre-installed infrastructure like magnetic tapes or beacons make it highly scalable.
Technology
3D localisation is computationally intensive, and operating on raw 3D data real-time within an embedded system is challenging. Ceiling and ground optimisation (CGO) is employed to filter out unnecessary vertical information, reducing computational costs. Most autonomous mobile robots operate in a 2D plane, making vertical data less relevant for horizontal localisation. Dimension reduced fusion and mapping (DRFM) integrates 3D localisation and obstacle information into a dimension reduced map (DRM), significantly improving computational efficiency. Navigation is performed based on the DRM, enabling real-time operations.
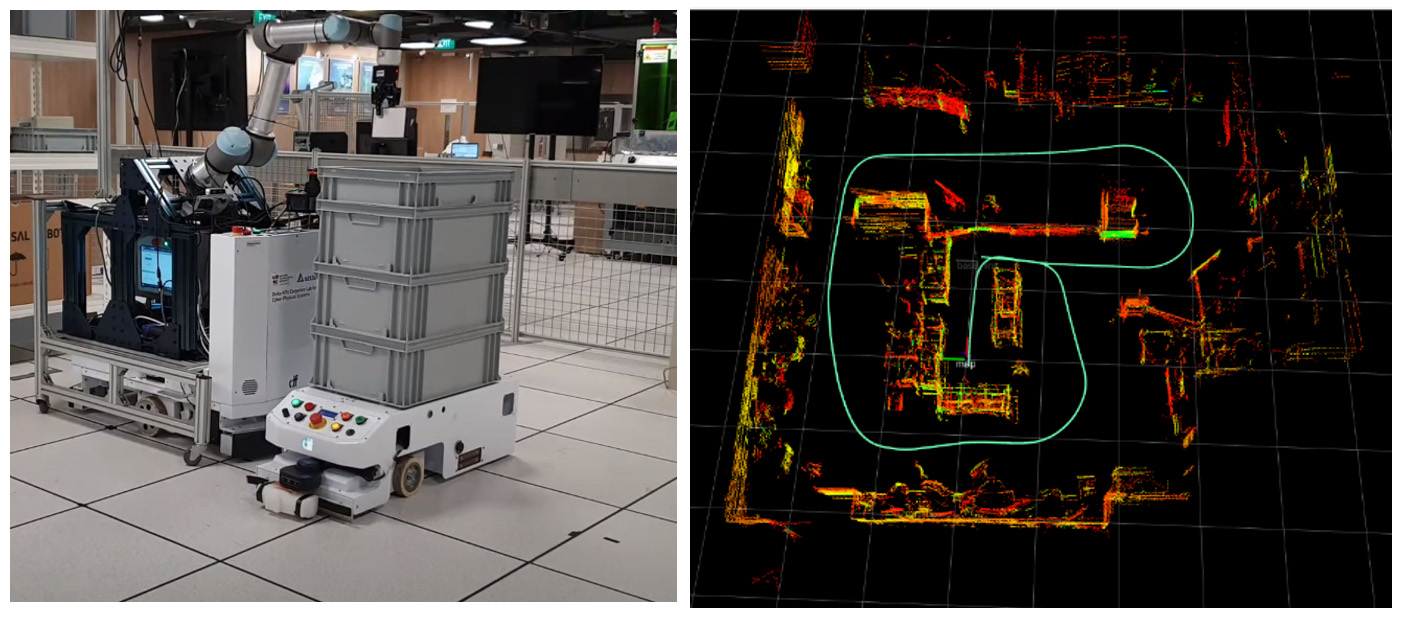
Figure 1: 3D LiDAR based autonomous navigation for indoor mapping and multi-robot collaboration. Left image is the multi-agent transportation and right image is the cm-level indoor localisation and mapping.
Applications & Advantages
Main application areas include warehouse management, distribution centres and industrial automation.
Advantages:
- Achieves up to 1 cm accuracy with CGO, running at 10 Hz on an embedded system.
- DRFM fuses 3D localisation and obstacle information into DRM, enhancing computational efficiency.
- Operates effectively in 3D space, ensuring safe navigation.
- Adaptable to various lighting conditions without reliance on pre-installed infrastructure.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=57e7d9a3_1)


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)







