
Mutual Authentication and Key Exchange Protocol for Peer-to-Peer
Synopsis
This technology offers a lightweight and secure protocol for mutual authentication directly between two peer-to-peer (P2P) Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices. It uses puzzles solvable only by genuine interlocutors through physically unclonable functions (PUF), without storing any secrets on the device.
Opportunity
Currently, IoT devices connect indirectly through a server, requiring data collected on one device to flow to the server before reaching another device. P2P IoT enables direct data sharing between two peers, significantly lowering latency and enhancing privacy compared to database-driven IoT. However, the current approach of using a server to mediate direct end-to-end encrypted connections between two IoT endpoints is complex and inefficient.
Technology
This technology offers a solution by providing a lightweight and secure protocol for mutual authentication and key exchange directly between two endpoints in P2P IoT. The protocol leverages PUFs, derived from manufacturing process variations of integrated circuits, as device “biometrics”. The PUF circuit embedded in an endpoint device generates a unique, unpredictable and unforgeable identity upon query. PUF-based device identity is tamper-aware and more secure than hardcoded or memory-based identities. This protocol enables any pair of IoT devices, once enrolled, to directly authenticate each other. Upon successful authentication, a secure and fresh shared session key is automatically established for encrypted communication.
This protocol employs a hardware-intrinsic root of trust to ensure robust security and privacy protection against impersonation attacks. It creates puzzles solvable only by genuine interlocutors using their respective PUFs (“silicon biometrics”), ensuring that secrets are not stored on the device. The secret required to solve the puzzle is generated upon request by the device PUF, making it tamper-proof.
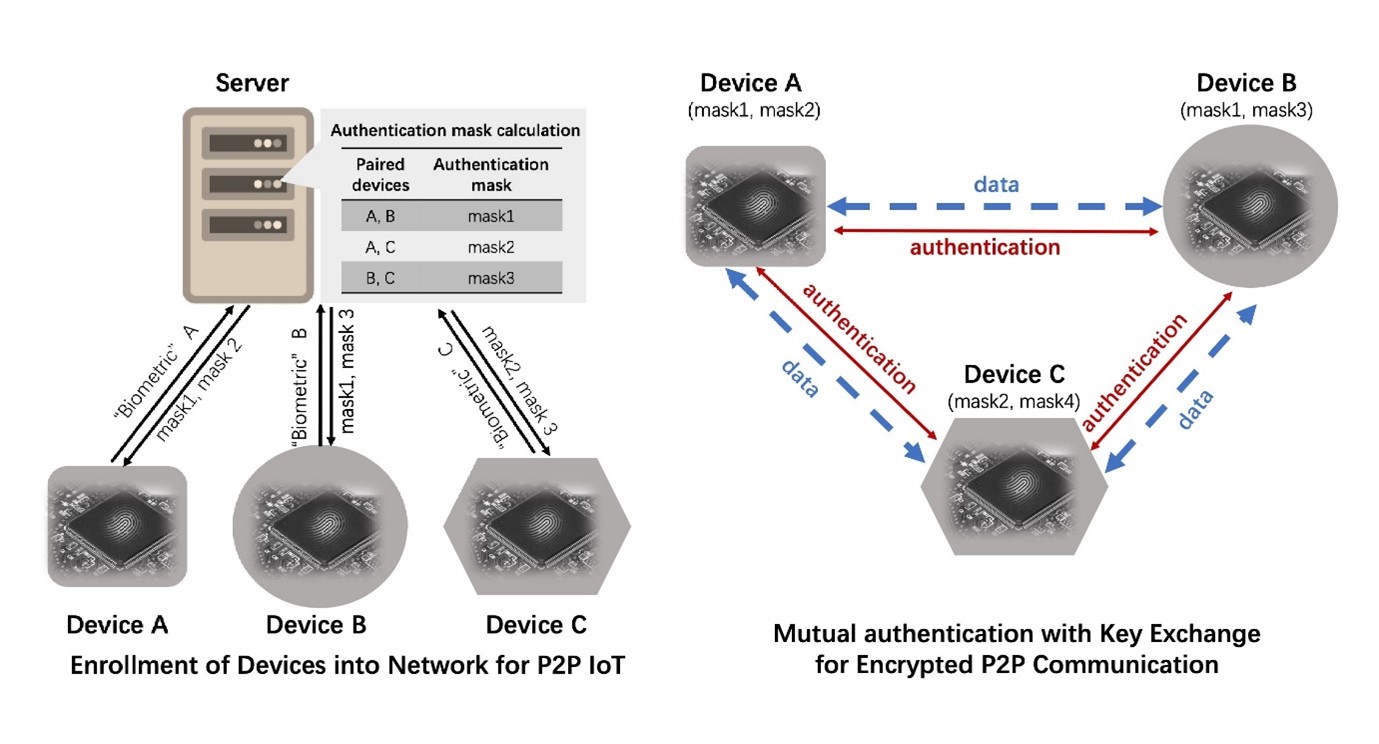
Figure 1: Overview of Mutual Authentication with Key Exchange for P2P Communication.
Applications & Advantages
Main application areas include smart home systems and secure peer-to-peer communications in IoT applications, as well as drone remote control, surveillance and secure communication between a window actuator and its external weather station.
Advantages:
- IoT devices do not need to store any secrets locally. Device-to-device mutual authentication and key exchange can be achieved directly without involving a server after enrolment.
- “Silicon biometrics” can be realised in several ways, such as memories or ring oscillators, based on the resources of each device.
- Only three handshakes are required to establish mutual authentication and key exchange.
- The total communication cost for each pair of devices is around 300 bytes and the storage cost on each device is around 150 bytes.
- The handshake messages are generic, allowing adaptation to any payload of gateway or network communication package specifications.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=414f0d90_1)







