
System and Method for Automated Guided Vehicles Fleet Management
Synopsis
This novel automated guided vehicle (AGV) fleet management system enhances automation in manufacturing, logistics and warehouse operations. It integrates task management, battery recharge and path planning to optimise AGV utilisation, focusing on efficiency and adaptability. Key features include just-in-time task assignment, flexible charging and dynamic path planning, addressing automation challenges and ensuring robust operation in dynamic environments.
Opportunity
The demand for increased automation in manufacturing is rapidly escalating in the Industry 4.0 landscape. Efficient, robust and cost-effective systems are crucial, particularly in deploying AGVs for seamless material and product transportation. A critical challenge is ensuring continuous AGV operation despite varying battery levels and unpredictable demand. Existing warehouse automation solutions have addressed AGV coordination and task assignment, but further optimisation is needed. This invention introduces a sophisticated AGV fleet management system, employing a hybrid receding horizon/incremental scheduling strategy to enhance robustness against environmental uncertainties.
Technology
The AGV fleet management system integrates three key modules: Task Management, Battery Recharge Management and Path Planning. The Task Management module prioritises idle AGVs with ample battery charge through just-in-time task assignment based on energy and delivery time analysis. The Battery Recharge module optimises recharge sequences, reducing downtime and minimising recharge population. The Path Planning module utilises the A* algorithm with a hybrid receding horizon/incremendal scheduling approach, coordinating paths to mitigate bottlenecks, minimise transit times and handle environmental uncertainties. This comprehensive technology suite ensures efficiency, adaptability and resilience in automated vehicle operations.
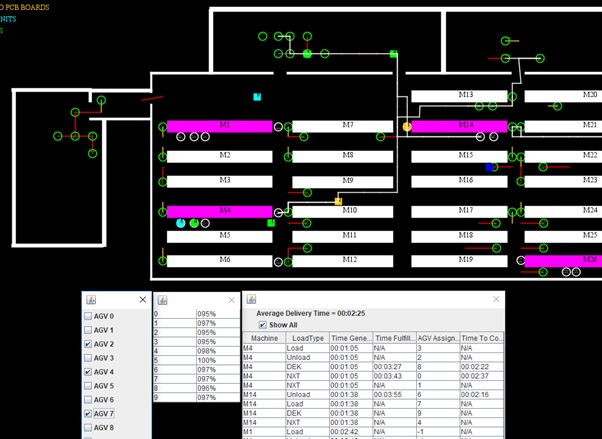
Figure 1: Dynamic task management, battery recharge management, and path planning.
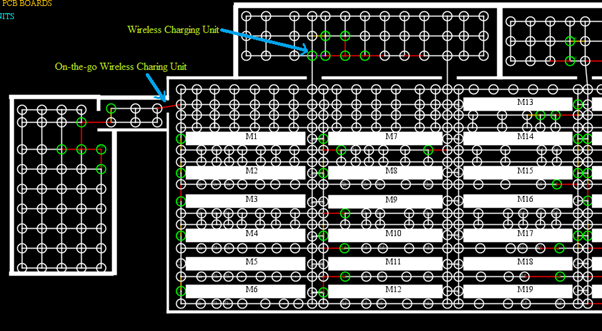
Figure 2: Optimised charging unit and on-the-go location.
Applications & Advantages
Applications
- Manufacturing Industry: Optimises material and product transportation in factory settings.
- Logistics: Enhances efficiency and adaptability in AGV fleet management for timely deliveries.
- Warehouse Automation: Streamlines task assignment, battery recharge and path planning for improved overall performance.
Advantages
- Efficiently assigns tasks based on delivery time and AGV battery charge.
- Adaptable charging logic for AGVs, considering available wireless charging units.
- A* algorithm with hybrid receding horizon/incremental scheduling for effective coordination and adaptability in dynamic environments.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=414f0d90_1)








