
Photodynamically Active Organosilica Nanoparticles and Their Medical Applications
Synopsis
This invention introduces photodynamically active mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles (PcNP) for melanoma therapy. PcNP has shown efficacy in combinational photodynamic and drug therapy, validated through 3D tumour models and porcine skin penetration tests. In vivo studies further confirm its potential, heralding a promising advancement for melanoma treatment.
Opportunity
Skin cancer, characterised by the abnormal growth of skin cells, most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. The global skin cancer treatment market size was valued at $7.2 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $14.5 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7.3% from 2022 to 2031. Key factors driving this growth include the rise in incidence of melanoma and non-melanoma types of cancer and the increased demand for better treatments. Novel skin cancer treatments with higher efficacy and fewer side effects are expected to provide significant market opportunities.
Technology
This groundbreaking invention introduces PcNP, a significant advancement in combinational cancer therapy targeting melanoma. PcNP demonstrates exceptional efficacy in combinational photodynamic therapy (PDT) and drug therapy.
The unique properties of PcNP have been rigorously tested across multiple dimensions. Its efficacy has been demonstrated in 3D tumour spheroids, showcasing its ability to penetrate and exert therapeutic effects in complex structures. Additionally, PcNP has shown remarkable topical penetration on porcine skin, highlighting its potential for transdermal drug delivery using microneedles.
Furthermore, in vivo studies have demonstrated PcNP’s antitumoral efficacy studies in a mouse model, solidifying its potential as a promising therapeutic agent against melanoma. The successful outcomes across these testing scenarios underscore PcNP’s versatility and robustness in addressing melanoma through a synergistic combination of PDT and drug therapy.
This innovative nanoparticle holds significant promise for advancing melanoma treatment, offering a multifaceted approach that combines precise targeting, therapeutic efficacy and minimally invasive delivery methods for improved patient outcomes.
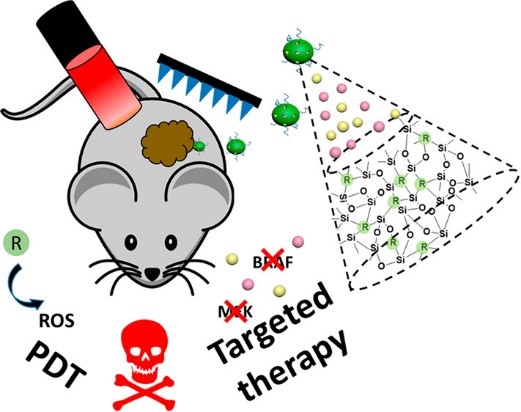
Figure 1: Photodynamically active mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles are synthesised with photosensitisers covalently bonded to the silica matrix, which could dramatically increase the quantum yield and photostability of these photosensitisers. The mesopores of the nanoparticles could be further loaded with small-molecule drugs. As-prepared empty nanoparticles are cytocompatible with normal cells in the dark, while NIR-irradiated drug-loaded nanoparticles show a synergistic killing effect on cancer cells mainly through photodynamic therapy (PDT). When applied topically, microneedle technique could facilitate the penetration of nanoparticles across the epidermis layer of skin to reach deep-seated melanoma sites for the treatment.
Applications & Advantages
Main application areas include topical treatment of cancer, such as melanoma.
Advantages:
- Exhibits low cytotoxicity in the dark and is biocompatible.
- Small size (~30nm) for efficient topical drug delivery.
- Capable of high photosensitiser loading without aggregation-induced quenching.
- Offers a higher loading capacity of anti-cancer drugs, with the photosensitiser integrated as part of the nanoparticle structure.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=a0428bd8_1)


-with-those-from-other-fungi.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3025740f_1)








