
Method for Optimal Placement of On-the-Go Wireless Charging Units
Synopsis
The automated guided vehicle fleet management system (AGVFMS) revolutionises Industry 4.0 manufacturing automation. This system optimises AGV fleet operations through dynamic task assignment, intelligent recharge strategies and adaptive path planning. Featuring on-the-go wireless charging and a mixed integer linear programming (MILP) algorithm for cost-effective solutions, it enhances AGV fleet efficiency and minimises operational delays.
Opportunity
In the Industry 4.0 landscape, there is a rising demand for efficient, robust and cost-effective automation in manufacturing. The AGVFMS meets this demand by enhancing AGV fleet management with dynamic task assignment, intelligent battery recharge strategies and adaptive path planning. This technology ensures timely, energy-efficient transportation of materials and products, which is critical for meeting unpredictable demand and stringent deadlines. The integration of on-the-go wireless charging eliminates factory delays associated with AGV battery recharge. The MILP algorithm ensures optimal placement, underscoring the technology’s economic viability and advanced capabilities for diverse manufacturing and logistics applications.
Technology
This advanced technology centres on AGVFMS comprising three integrated modules: Task Management, Battery Recharge Management and AGV Path Planning. The Task Management module assigns tasks to AGVs based on object type, locations and delivery times. It employs a just-in-time assignment strategy, considering both the AGV's capability and battery charge, optimising energy usage and minimising delays. The Battery Recharge Management module utilises on-the-go wireless charging units to prevent delays from battery charging. These units are strategically placed using a MILP algorithm, ensuring optimal coverage and efficient charging within budget constraints. The AGV Path Planning module leverages the A* algorithm with a hybrid receding horizon/incremental scheduling strategy, enabling AGVs to adapt paths dynamically based on real-time conditions and trajectories of other AGVs.
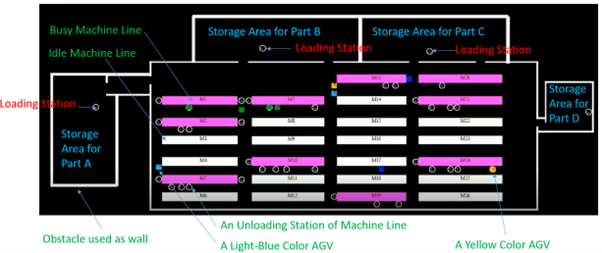
Figure 1: Factory layout example (in simulation).
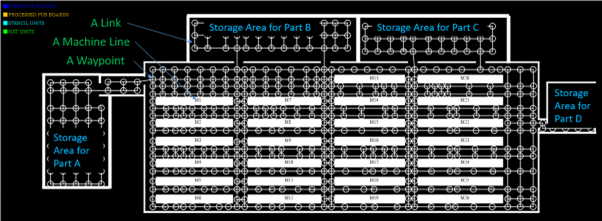
Figure 2: Factory layout example (before simulation).
Applications & Advantages
Applications
- Manufacturing Optimisation: Ideal for industries like PCB production, where AGVs handle complex material tasks.
- Logistics Efficiency: Enhances AGV fleet performance in scenarios with varied tasks and operational constraints.
- Dynamic Charging Solutions: On-the-go wireless charging units enable continuous AGV operation, minimising factory delays.
Advantages
- On-the-go wireless charging units charge AGVs while in motion, reducing or eliminating delays related to battery recharge.
- MILP algorithm optimises the placement of wireless charging units, ensuring efficient coverage without unnecessary expenses.
- Simulations show improved delivery times and sustained battery levels, validating the effectiveness of on-the-go wireless charging in AGV fleet management.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=414f0d90_1)








