
Site-Specific Induction of Bimolecular Quadruplex-Duplex Hybrids and Their Applications
Synopsis
This invention presents antisense oligonucleotide therapeutics that induce biomolecular quadruplex-duplex hybrids, providing a novel method for modulating gene expression and regulatory processes to achieve targeted cancer treatment.
Opportunity
The global cancer therapeutics market size is projected to reach US$ 393.6 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 9.20% from US$ 164 billion in 2022. The rise in cancer prevalence and the ageing population are major factors driving the growth of the cancer therapeutics market, creating a need for novel and effective therapies. Antisense technology, utilising the complementary hybridisation of an antisense oligonucleotide, shows promise as a novel therapeutic approach—but targeted delivery remains a significant challenge.
Technology
This invention focuses on antisense oligonucleotide therapeutics, specifically controlling nucleic acid structures to induce a bimolecular quadruplex-duplex hybrid. This hybrid formation occurs between an isolated oligonucleotide molecule and a target nucleic acid molecule, and is facilitated by the direct connectivity between duplex and quadruplex structural elements.
By manipulating nucleic acid structures in this manner, the invention offers a novel approach to modulating gene expression and regulatory processes. The induction of a bimolecular quadruplex-duplex hybrid presents opportunities for precise targeting of specific nucleic acid sequences, with potential applications in gene therapy, RNA interference and molecular diagnostics.
This technique enhances the specificity and efficacy of antisense oligonucleotide therapeutics, paving the way for more targeted and personalised treatment strategies. Leveraging the direct connectivity between duplex and quadruplex structural elements, the invention opens new avenues for controlling gene expression and modulating biological processes at the molecular level.
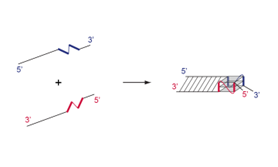
Figure 1: G-quadruplexes (G4) are helical structures formed from the association of four tracts of contiguous guanines. This invention presents an approach to induce the formation of G4 from two complementary sequences, which combines the specificity of Watson-Crick base pairing with the stability associated with robust G4 scaffold.
Applications & Advantages
Main application areas include the development of cancer therapeutics, research and diagnostic tools.
Advantages:
- Offers a novel platform for cancer therapy by modulating gene expression and regulatory processes.
- Enhances the specificity and stability of antisense drugs binding.
- Enables precise targeting of specific nucleic acid sequences, improving therapeutic outcomes.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=a0428bd8_1)


-with-those-from-other-fungi.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3025740f_1)








