
A β-Peptido-Sugar-Copolymer
Synopsis
The rise of antimicrobial resistance poses a global threat. This invention introduces synthetic mimics of antimicrobial peptides (SMAMPs), crafted from helical block-like copolymers. With potent antimicrobial properties, these SMAMPs offer targeted bacterial killing, especially against Gram-positive bacteria like Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Their efficient synthesis method ensures scalability, promising advancements in medical antimicrobial technologies for various applications, from wound care to medical device coatings.
Opportunity
The global antimicrobial drugs market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 2.6% from 2021 to 2031, reaching a valuation of over USD 62 billion by 2031. Antimicrobial resistance is a global threat, driven by the extensive use of antimicrobial drugs in human and animal health. Without the development of new drugs, the expansion of resistance will continue, diminishing the effectiveness of current treatments and leaving many patients with limited treatment options. This challenge underscores the critical need of a novel approach to combat bacterial infections.
Technology
This invention introduces a novel class of SMAMPs, characterised as helical block-like copolymers. These copolymers, comprising poly-β-(L)-HOMOLYSINE (PBLK) and helical poly-amido-D-glucose (PDGu), are synthesised using a one-pot anionic ring-opening polymerisation (ROP) technique.
The dual components of these copolymers play distinct yet complementary roles in their antimicrobial function—with PBLK demonstrating efficacy in bacterial killing, particularly against Gram-positive bacteria, showcasing its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Meanwhile, PDGu ensures selectivity and biocompatibility. The one-pot anionic ROP synthesis method ensures a streamlined and efficient production process, facilitating scalability and practicality for medical applications.
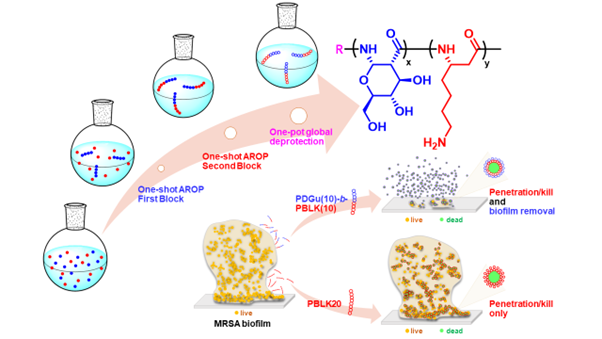
Figure 1: An antimicrobial peptidomimetic block-co-beta-peptide, synthesised by a facile one-shot one-pot polymerisation process, disperses biofilm matrix and kills methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria.
Applications & Advantages
The main application area of this invention is in medicine as an antimicrobial agent, for instance in wound care or in medical device coatings.
Advantages:
- Biocompatible
- High microbial activity
- Effective against Gram-positive bacteria, including Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- Demonstrates superior efficacy compared to Vancomycin for MRSA in mouse models for both anti-bacterial and anti-biofilm activities


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=a0428bd8_1)


-with-those-from-other-fungi.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3025740f_1)








