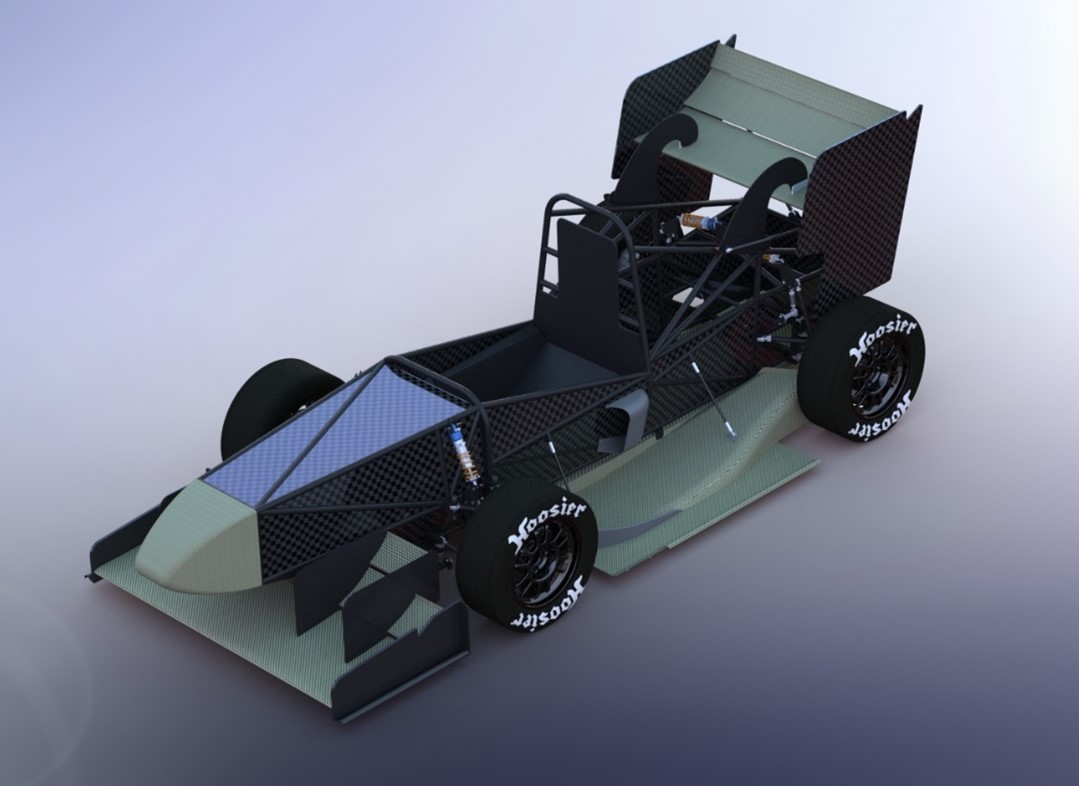
Nanyang Venture Formula 1 (NVF1)
Materials and Key Features
NVF 1 is made up many different materials:
- Chassis: Welded chromoly Steel tubing
- Body panels: Carbon fibre foam sandwich construction
- Aerodynamic parts: Carbon Kevlar foam sandwich construction
- Fully electric using Lithium Iron Phosphate cylindrical cells
- Many 3D Printed Elements
- Touchscreen driver information display
- Range for competition: 80 km at cruise
- Total Weight: 390kg
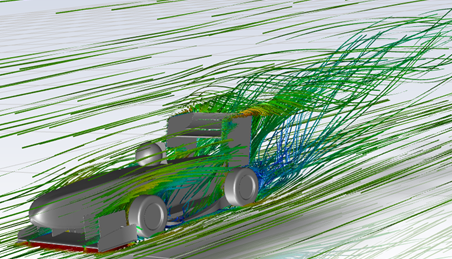
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a key factor in the design and performance of the NVF 1 race car. The shape and design of the car's body and wings have significant impact on the car's handling, stability, and speed by controlling the
aerodynamic downforce.
To optimize the aerodynamics, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations were performed to analyse the flow of air around the car and determine the best shape and placement of the various aerodynamic components. The team manufactures all the mould and carbon fibre parts such as front and rear wing packages and undertray diffusers to a high quality and workmanship.
 |  |
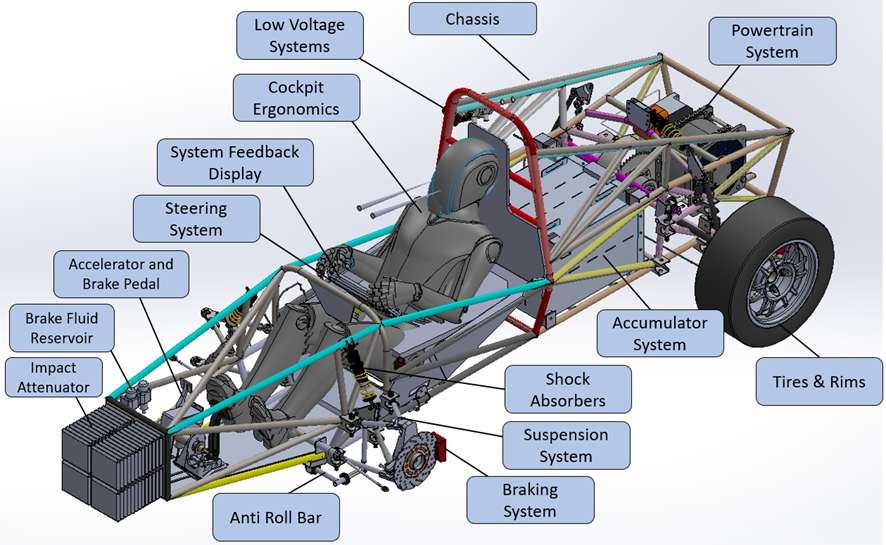
Vehicle Dynamics, steering and suspension
Vehicle dynamics has to do with the design, analyses and optimisation of the handling and performance of the race car. Various tools and techniques are used to understand the dynamic behaviour
of the car and identify opportunities for improvement.
Computer simulations, physical testing, and data analysis to study the car's handling characteristics, such as its tire grip, balance, stability, and aerodynamics are key aspects.
The team is responsible for suspension and steering design, setting of shock absorbers, such as tire pressures to optimize the car's handling for specific tracks and conditions.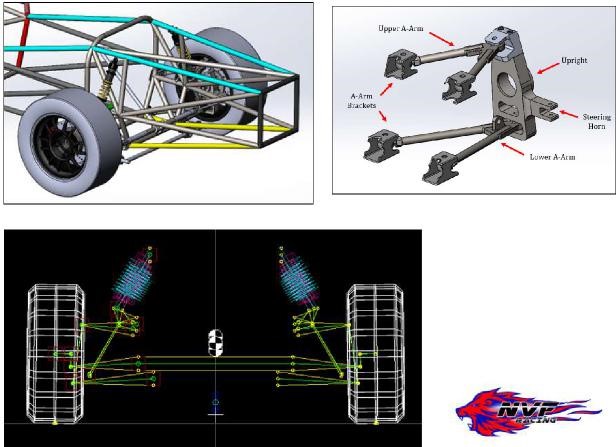
Drive train, hydraulics, brakes and wheels
The drive train is a group of components which deliver power from the battery (energy source), convert to mechanical energy via the electric motor and gear box and then deliver it to the
road wheels via drive shafts. The hydraulic braking system ensure that the vehicle will stop safely when commanded.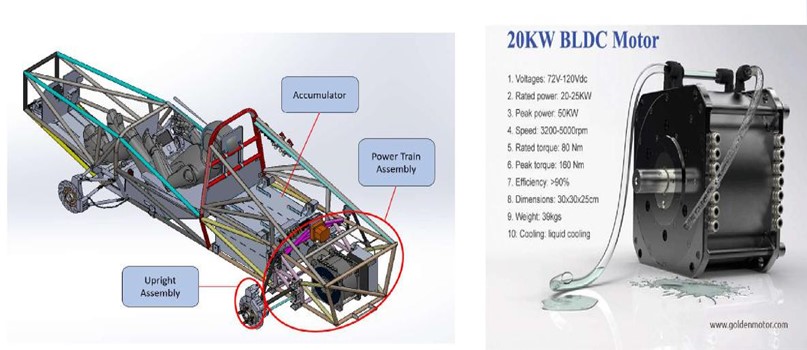
Welded Chassis - Stress Analysis and Fabrication
The chassis is the structural frame that holds the engine, suspension, and other components. The chassis must meet the required
performance and safety standards, as well as the team's design goals. Computer-aided design (CAD) software was used to create 3D models of the chassis and simulate its performance using finite element analysis (FEA). The team manufactured the chassis
using jig and fixtures and CNC bending. This involved cutting and forming the chassis components using CNC machines, and then welding or fastening the components together to form the complete chassis.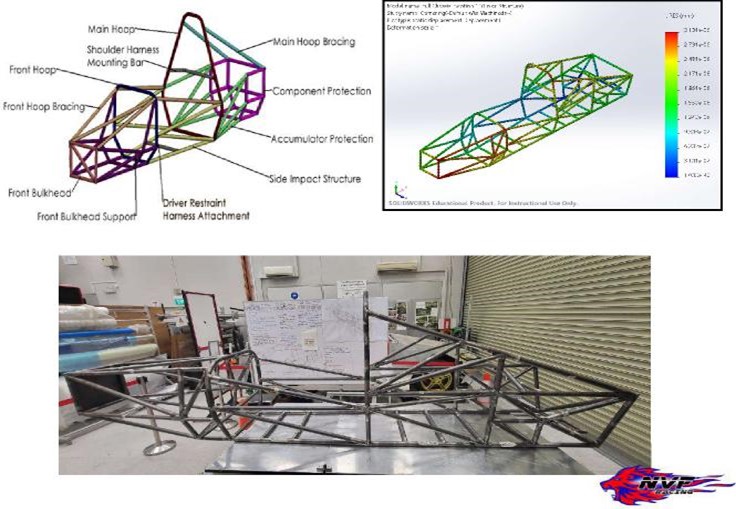
Electrical and Electronics
The electrical systems provide a reliable and efficient power source and control system for the various systems and components on the car, while also collecting and transmitting data to help the team optimize
the car's performance.
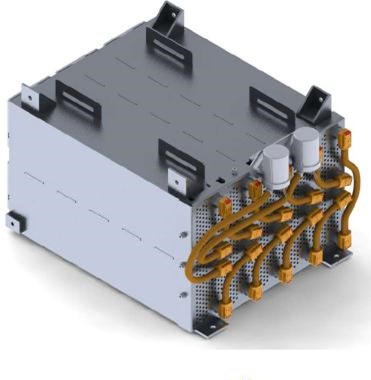
- Battery: A high-performance battery is used to store electrical energy and provide a power source for the car's systems.
- Power distribution: A power distribution system is used to route electrical power from the battery to the various systems and components on the car, such as drive motor and controller.
- Electrical safety system: a comprehensive rule based safeguarding and emergency shutdown system involving sensors, battery management system and array of fuses, relays, lighting and wiring harnesses.
- A data acquisition system is used to collect and transmit information about the car's performance and operating conditions, such as engine RPM, speed, temperature and energy consumption.